Новости
Обратите внимание, что приведенные данные точны на момент публикации и могут быть изменены в будущем без уведомления. На этой странице показаны только самые последние элементы. Для получения полного архива пресс-релизов нажмите «Поиск по категории или году».
Mitsubishi Electric Achieves World’s First Mechanism for Elucidating Ozone Oxidation Enhanced with Negative Ions (на английском языке)
Use of negative ions to enhance ozone oxidation and reduce pink slime yeast
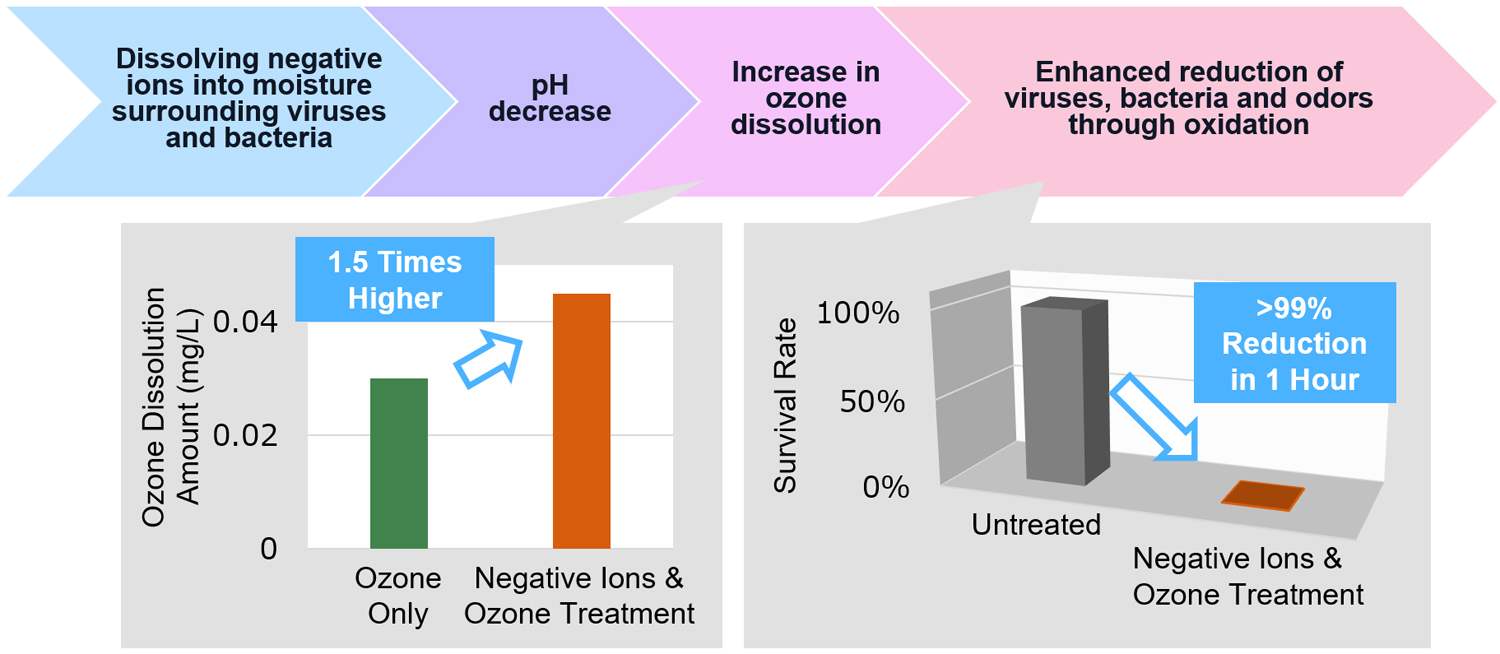
TOKYO, December 15, 2025 - Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (TOKYO: 6503) announced today that in collaboration with Professor Toshiaki Kamachi and colleagues from the School of Life Science and Technology at Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) they have achieved the world’s first1 mechanism for elucidating the combined use of negative ions to enhance the oxidative action of ozone. In their joint study, they discovered that dissolving negative ions in the moisture surrounding viruses and other microorganisms lowers the pH due to nitrate-containing components derived from the negative ions, which in turn enhances the oxidative action of ozone in the moisture, enabling a strong reduction of viruses and bacteria even at low ozone concentrations. Mitsubishi Electric confirmed the reduction of bacteria and odors in low ozone concentrations of 50 parts per billion (ppb)2 in addition to specific viruses reported previously.3
Buildings are becoming more airtight and better insulated, raising concerns about inadequate indoor ventilation and unhygienic conditions. Ozone’s oxidative action has traditionally been used to maintain indoor hygiene, but ozone alone has faced challenges in terms of the durability and stability of its sanitizing effects. It is also known that ozone’s reduction of viruses and bacteria increases when used with negative ions and varies with pH. However, the specific chemical species of the negative ions and their pH-controlling effects had not been clarified.
Using Mitsubishi Electric’s established technologies to evaluate the reduction of viruses, bacteria and odors, together with Science Tokyo’s analytical and identification capabilities for discharge-generated reactive species,4 the two organizations clarified how negative ions control pH in aqueous films. They also elucidated the mechanism by which the combined use of negative ions enhances ozone’s oxidative action, and additionally confirmed that adherence of Escherichia coli and pink slime yeast to test specimens in wet areas was reduced by 99% within one hour, and that sweat and damp-clothing odors were reduced by at least one unit of odor intensity within one hour.5
Details will be presented at the Pacifichem6 2025 international conference in Honolulu, Hawaii from December 15 to 20.
Going forward, Mitsubishi Electric will continue to develop innovative technologies for safer and more enjoyable indoor environments.
- 1
According to Mitsubishi Electric research as of December 15, 2025.
- 2
The Japan Air Cleaning Association—Air quality standards gases in the general office room: the average ozone concentration should be approximately 50ppb or less.
- 3
Tests were carried out in a 23m3 test chamber, following JEM1467 and the procedures described in the Journal of the Society for Antibiosis and Mycology, Vol.52, No.2 (2024), using metal coupons onto which a viral suspension had been deposited.
- 4
Reactive species generated by discharge (including electrons, ions, radicals and excited-state molecules)
- 5
Evaluated on a six-point scale of odor intensity, with a one-unit decrease corresponding to a 90% reduction in perceived odor.
- 6
One of the world’s largest international conferences in the field of chemistry, held every five years https://pacifichem.org
Inquiry
-
Customer Inquiries
Advanced Technology R&D Center
Mitsubishi Electric CorporationFax: +81-6-6497-7285
https://www.MitsubishiElectric.com/ssl/contact/company/rd/form.html
Поиск по категории или году публикации
Нет статей для указанного вами состояния.
